-
 featured
featured May 5 - May 5, 2026
Plus 3 other start datesSep 2 - Sep 2 2026
Jan 5 - Jan 5 2027
May 4 - May 4 2027
Tuition
$2,499
Scholarships available
-
 featured
featured Sep 2 - Sep 2, 2026
Tuition
$4,944
Scholarships available
-
featured
Online
May 5 - Jan 5, 2026
Plus 3 other start datesSep 2 - May 2 2026
Jan 5 - Sep 5 2026
May 4 - Jan 4 2027
Tuition
$7,808
-
 featured
featured May 5 - May 5, 2026
Plus 2 other start datesSep 2 - Sep 2 2026
Jan 5 - Jan 5 2027
Tuition
$7,809
Scholarships available
About
As cybersecurity threats increase in volume and severity worldwide, so does the demand for skilled professionals who can prevent and mitigate cyberattacks that take businesses offline, halt productivity, and incur severe financial losses.
With a shortage of cybersecurity talent in Canada and worldwide, cybersecurity professionals are in high demand across the public and private sectors. According to the Canadian Job Bank, cybersecurity will continue to face a national labour shortage for the next five years. The federal government anticipates more than 143,000 new job openings for information systems analysts and consultants between 2022 and 2031, in addition to the 288,000+ existing roles.
Cybersecurity is the practice of safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring the integrity of computer systems, data, and networks – a field with abundant job opportunities, since nearly all companies rely on digital technology and data to operate.
Canada’s leading cybersecurity courses, security training programs, and cybersecurity certifications will teach you how to identify and manage security threats that risk putting critical private, business and government information in the wrong hands. You’ll learn how to safeguard software programs, computer networks, and hardware devices against breaches from malicious hackers while joining one of North America’s fastest-growing workforces. Top programs offer a mix of foundational theory and practical training through co-ops, internships or capstone projects.
Salaries in this job category range depending on your skillset and level of responsibility. Entry-level cybersecurity engineers and analysts make between $64,000-$69,000 on average, according to Indeed.com and Glassdoor, but with a few years of experience can quickly earn upwards of $80,000-$100,000, alongside cybersecurity consultants, specialists and testers. Chief Information Security Officer salaries range from $120,000 to well over $200,000.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What skills do you need to work in cybersecurity?
You’ll need technical and problem-solving skills to become a cybersecurity expert. However, the specific competencies you’ll need will depend on the size and type of company that employs you. For example, someone in a network security role at a small company or organization might be expected to secure basic network infrastructure. Larger organizations might require expertise in managing and designing network security architecture.
Cybersecurity experts should have a foundational understanding of networking, cloud computing, and network topologies, knowledge of program syntax, familiarity with operating systems and how they work, and an understanding of VPNs, anti-virus principles, and firewalls.
Soft skills that will make you an ideal candidate for a job in cybersecurity include good oral and written communication skills, especially when it comes to explaining technical issues to those who aren’t tech-savvy, as well as good problem-solving abilities and the tenacity to work well under pressure.
-
What are the in-demand certifications for cybersecurity jobs?
CompTiaSecurity+ is an internationally-recognized certification that validates baseline cybersecurity skills. With the Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) designation, you’ll learn how to assess risk, respond to incidents proactively, and implement enterprise governance.
The Certified Information Security Auditors (CISA) is a global certification for professionals conducting audits to assess IT and business systems within an organization.
Additionally, the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) requires 5+ years of work experience and showcases a cybersecurity professional’s ability to lead information security initiatives within an organization.
Here, you can learn more about the best cybersecurity certification programs of 2024.
-
What cybersecurity career paths are there?
There are many different career paths within the cybersecurity field, many of which largely fall into two categories: “generalists” and “specialists”.
Generalists have broad knowledge and skill sets and are expected to juggle multiple responsibilities. For example, they might oversee security measures or encryption protocols. Project managers, analysts, auditors, and support staff are some of the titles associated with cybersecurity generalists.
A generalist path might be best suited for someone seeking to rise to the management ranks, which often requires a broad knowledge of the various aspects of information security to make informed, strategic decisions alongside a number of teams.
On the other hand, specialists usually have expertise in specific tools and technologies, with advanced knowledge in a specific niche within the cybersecurity field. For example, an Identity and Access Management (IAM) Specialist focuses mainly on managing and controlling user access to systems, data, and applications within an organization. Meanwhile, someone specializing in penetration testing will simulate cyber attacks to identify weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications before malicious hackers can exploit them.
A specialist path allows you to develop niche expertise that few others have, which can give you a competitive edge in the job market.
Certification
Most employers require their cybersecurity employees hold a bachelor’s degree or diploma in computer science, computer security, computer systems engineering, or information technology systems. That said, because cybersecurity is such a rapidly evolving field, there is a constant need to update your skills, which is where the best cybersecurity certification programs are incredibly useful.
To be successful in this area of work, you will first need to understand the fundamentals of information technology, such as administering and configuring systems, networks, database management and coding. A foundation degree or diploma will give you the basis to build your understanding of the demands of security protocols and the wide range of potential threats that are constantly evolving.
Following this, certificates deliver tailored instruction and hands-on training to help you navigate cyber attack scenarios in increasingly complex case studies, using the latest technology.
There are a wide range of recognized certifications available in cybersecurity which can be obtained online or from a number of institutions, including those offered by some of the biggest names in the business, such as Cisco and McAffee, as well as globally recognized certification bodies, such as CompTIA and ISACA.
The following are some of the more popular and well-known cyber certifications available:
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Information Security Auditor (CISA)
- CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+)
- CompTIA Cyber Security Analyst (CySA+)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Cyber Security Nexus Practitioner
The internet is only as safe as the people, code, and measures that defend it. This intensive 12-week gives students the fundamental knowledge, real-world experience, and critical soft skills needed to kickstart a rewarding career in cyber security. This program … Continue reading
Tuition
$14,000
Scholarships available
Tuition
$14,000
Scholarships available
Learn in-demand skills to launch a new career in cybersecurity with BrainStation’s immersive bootcamp. Passwords, antivirus software and other tools are an important part of remaining secure, but ultimately, it’s the right mindset and a strong foundational knowledge that defines … Continue reading
Tuition
$16,500
Scholarships available
Tuition
$16,500
Scholarships available
Centennial College’s Cybersecurity program is a one-year Graduate Certificate program designed to address the industry’s increasing demand for well-educated security professionals in the public and private sectors. This graduate certificate program will educate learners on how to protect computers, applications, … Continue reading
This two-term Ontario College Graduate Certificate will teach you technical and risk management skills that enable organizations to assess, develop, and enhance both preventative and responsive approaches to mitigating cyber-attacks. You will be taught how to take on mission critical … Continue reading
May 5 - May 5, 2026
Sep 2 - Sep 2 2026
Jan 5 - Jan 5 2027
Tuition
$7,809
Scholarships available
Tuition
$7,809
Scholarships available
Tuition & Completion Data
Domestic
Last updated: April 28, 2025
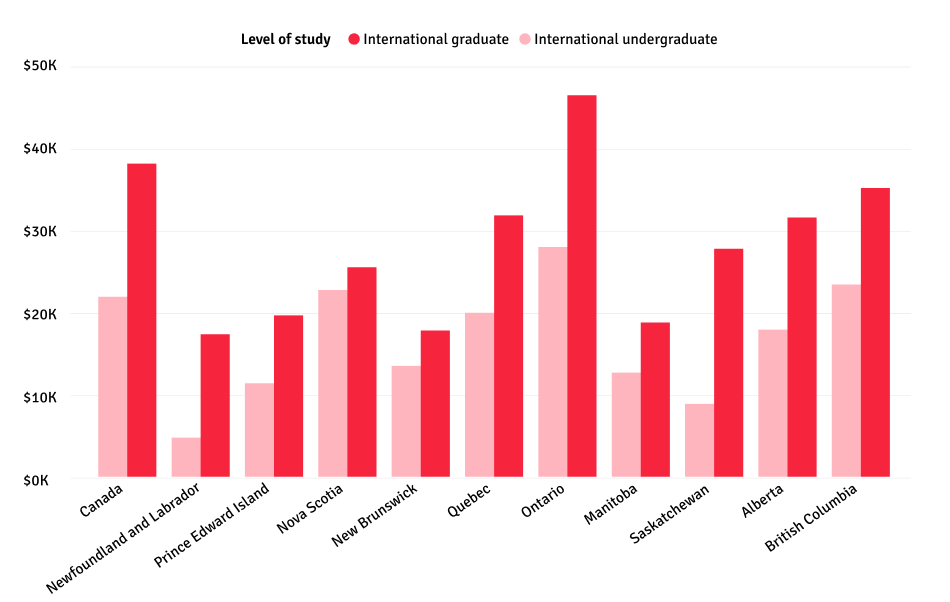
International
See below for the latest data on international student tuition across Canada, excluding housing costs and ancillary fees.
Source: Statistics Canada 2023
Careers
Professionals who work in cybersecurity perform a variety of roles including governing and supporting an organization’s technology infrastructure, protecting and defending it, designing and developing systems to support hardware, software and other systems as well as operating and maintaining these platforms.
Due to a worldwide shortage of IT security talent, cybersecurity professionals are in demand. Organizations like the Canadian Armed Forces actively recruit to fill the market and offer signing bonuses to non-commissioned members.
According to the Canadian Job Bank, the cybersecurity profession is expected to continue to face labour shortage conditions from now until 2031. That means there is ample opportunity for new graduates of cybersecurity training programs to land gainful employment in their field, in a variety of roles.
Security Engineer – $67,209
Security engineers focus on implementing security measures across an organization. They may troubleshoot new security measures, coordinate responses to security breaches and help the IT team develop ways to help avoid future issues.
Security Administrator – $69,033
Ensuring a company’s computer system is running optimally is the central role of the security administrator. This entails updating the system when needed, fixing issues and setting up new users as needed in a safe and secure manner.
Cybersecurity Consultant – $88,029
Cybersecurity consultants identify security issues, assess risks, and implement solutions. They perform tests to identify vulnerabilities while also designing and implementing strategies to improve organizational cybersecurity. Those who start as junior members of an IT team typically need one to three years of experience before taking on this role.
Cybersecurity or Penetration Tester – $96,675
In this role, performing simulated cyberattacks on an organization’s computer systems and network is par for the course to identify where there are vulnerabilities before cybercriminals do. The role requires advanced computer skills and a keen ability to anticipate a hacker’s actions.
Cybercrime Investigator / Digital Forensic Investigator – $102,764
This role requires investigating cybercrimes and working to stop cybercriminals, which can entail recovering data from computers and other digital storage media to be used as evidence in court, interviewing witnesses and determining which cyber incidents are violating laws. Investigators also work for law enforcement agencies, government, or private organizations.
Cybersecurity Manager – $100,543
In addition to protecting the organization’s computer network by troubleshooting issues, a cybersecurity manager may be responsible for directing other IT professionals working as a team to promote digital security in the company.
Cybersecurity Architect – $128,380
This technical role involves designing, implementing, and maintaining security solutions and infrastructure.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) – $179,557
A CISO is a senior-level executive who oversees a company’s information, cyber and technology security. The role also requires developing, implementing, and enforcing security policies.
Salaries
Salaries in this job category range depending on your skillset and level of responsibility. According to Indeed, as well as Talent.com, Glassdoor and the Canadian Job Bank, entry-level cybersecurity engineers and analysts make $65,000 annually, but with a few years of experience can quickly earn upwards of $80,000-$100,000, alongside cybersecurity consultants, specialists and testers. Here is a closer look at salary ranges based on job type and seniority:
| Role | Average Salary in Canada |
|---|---|
| Security Engineer | $67,209 |
| Security Administrator | $69,033 |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | $82,544 |
| Cybersecurity Consultant | $88,029 |
| Cybersecurity or Penetration Tester | $96,675 |
| Cybersecurity Manager | $100,543 |
| Cybercrime Investigator / Digital Forensic Investigator | $102,764 |
| Cybersecurity Architect | $128,380 |
| Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) | $179,557 |